Difference between revisions of "Zork"
(add freeware category and download link) |
(change to supported) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
platforms=DOS, PDP-6, PDP-10| | platforms=DOS, PDP-6, PDP-10| | ||
engine=[[Glk/ZCode|ZCode]], [[Glk/Glulxe|Glulxe]], [[Glk/TADS|TADS]]| | engine=[[Glk/ZCode|ZCode]], [[Glk/Glulxe|Glulxe]], [[Glk/TADS|TADS]]| | ||
support= | support=Since ScummVM 2.2.0| | ||
purchase=[https://ifdb.tads.org/viewgame?id=4gxk83ja4twckm6j Available for free<br />from IF Database]| | purchase=[https://ifdb.tads.org/viewgame?id=4gxk83ja4twckm6j Available for free<br />from IF Database]| | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Glulx Games]] | [[Category:Glulx Games]] | ||
[[Category:Freeware Games]] | [[Category:Freeware Games]] | ||
[[Category:Supported Games]] | |||
[[Category:TADS Games]] | [[Category:TADS Games]] | ||
[[Category:Z-machine Games]] | [[Category:Z-machine Games]] | ||
Revision as of 01:45, 23 July 2021
| Zork | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| First release | 1977 | |
| Also known as | Dungeon | |
| Developed by | Dave Lebling, Bruce Daniels, Marc Blank, Tim Anderson | |
| Published by | MIT | |
| Distributed by | MIT | |
| Platforms | DOS, PDP-6, PDP-10 | |
| Resolution | (unknown) | |
| Engine | ZCode, Glulxe, TADS | |
| Support | Since ScummVM 2.2.0 | |
| Available for Purchase |
Available for free from IF Database | |
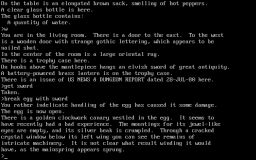
Zork is a text adventure that is the original first game in the Zork series.
Zork was developed on MIT's ITS operating system for the PDP-6 and PDP-10 mainframe computers, between 1977 and 1978 by MIT university students Dave Lebling, Bruce Daniels, Marc Blank, and Tim Anderson.
Versions
Zork was freely released on the ARPANET, the precursor of the internet. However, when three of the four designers of Zork formed Infocom, it was split into three text adventure games (Zork I, II, and III) so that it could be released commercially on the personal computer hardware of the time.
Volker Blasius ported Zork to DOS in 1987.
The original version of Zork has also been converted to several scripting languages:
- A TADS version was developed by Darin Johnson in 1996.
- A Glulx version was developed by Ethan Dicks in Inform 6 in 2004.
- A Z-code version was developed by Dean Menezes in Inform 7 in 2008.
It has been ported to other scripting languages such as Glulx, TADS, and Z-code.